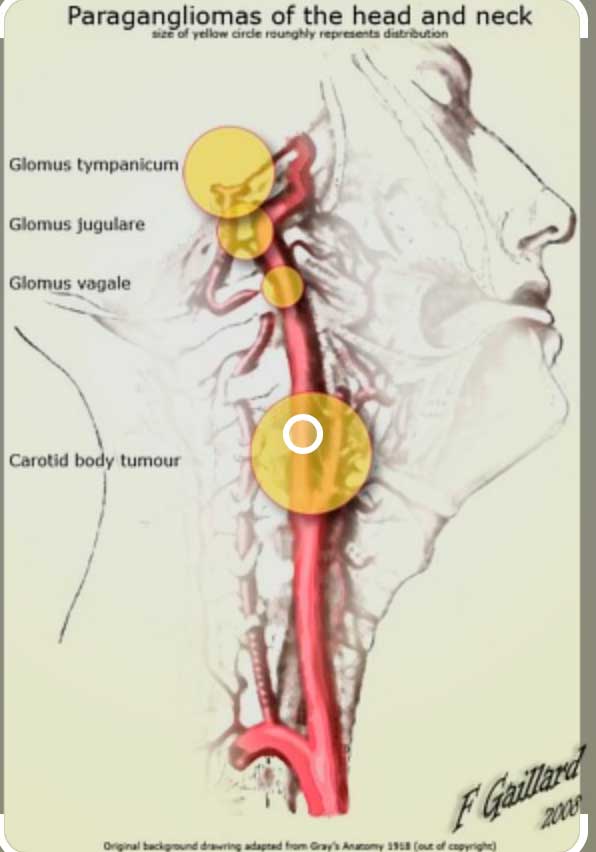
Glomus

Glomus of the temporal bone is the most common tumor in this location after acoustic neuroma. Glomus tumors are divided into two broad categories based on their place of origin, tympanic glomus and jugular glomus. Tympanic glomus is most often discovered after a patient suffers pulsatile tinnitus, an insidious type of conductive hearing loss. Sometimes it is discovered during a routine physical examination.
Jugular glomus arises from the dome of the jugular bulb and often appears later after it begins to grow and destroy bone. It can cause dysfunction in cranial nerves passing through the region of the jugular bulb (the 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th cranial nerves). It can also cause facial nerve paresis, which is weakness from nerve damage, or even hearing loss caused by inner ear bone erosion.
Glomus surgery is highly complex and time-consuming, but not all cases indicate surgery. After thorough evaluation and subsequent surgery, results are generally excellent.

